Poorly bent legs and inability to walk without support—all of which appear to be signs of aging, but in reality, they may be caused by disease. Knowledge about this disorder can help everyone, as timely treatment can prolong puberty in the joints. Knee joint disease has another name - joint deforming joint disease or osteoarthritis.
The disease belongs to the group of degenerative malnutrition diseases. Under the influence of pathogenic factors, joint tissue changes, and with this pathological change, not only the cartilage of the knee joint, but also bones, ligaments, joint capsules and the muscles that ensure their functioning are affected.
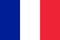
This disorder is one of the most common disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Due to changes in the tissue structure of hyaline cartilage, they lose elasticity, firmness and gradually collapse. This leads to an increased impact on the bone tissue, the so-called osteophytes. These are "thorns, " which are bone growths in the joints. If the arthropathy of the knee is not treated, the cartilage tissue may gradually disappear completely, the bones will deform, and the function and performance of the joint will be lost.
Causes of knee joint disease
The disease is classified as idiopathic, meaning that the etiology of knee osteoarthritis has not been precisely elucidated. There are two main types of arthropathy: primary and secondary.
Primary or idiopathic knee arthropathy of the knee develops due to metabolic and circulatory disturbances of the lower extremities. This form of the disease mainly affects older adults, especially women and people who are overweight. Degenerative dystrophic changes in cartilage tissue may be due to joint overloading, violation of normal blood circulation and multiple tissue microtrauma. Hormonal and endocrine disorders can also cause this.
Secondary or traumatic arthropathy occurs as a result of mechanical damage to the joint. This will result in:
- Knee injuries - knee ligament injuries, meniscus injuries, hemoarticular fractures and fractures;
- Various inflammatory diseases - rheumatism, arthritis;
- Non-inflammatory arthropathy - osteomalacia, arthropathy of various etiologies;
- Untimely and incomplete treatment of knee joint disease;
- Past trauma and injury.
symptoms of disease
Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis develop gradually. At the onset of the disease, pain occurs after physical exertion, overexertion, or long walks, followed by other symptoms and a detailed clinical presentation of the disease.
symptom:
- knee pain when moving;
- swollen joints;
- limited joint movement;
- stiffness of the knee;
- instability when leaning on a sore leg;
- Deformities of articular bones are visible.
Stages of Arthropathy
Clinically, there are several stages that reflect the severity of the disease:
- Stage 1 - Slight limitation of joint movement, increased limb fatigue, mild pain, appearing at the onset of exercise or after physical exertion, joint pain and stiffness disappearing at rest. The skeleton maintains its shape and is not deformed. X-ray showed a slight narrowing of the joint space.
- Stage 2 - Movement is significantly restricted, pain becomes constant when walking, especially exacerbated by physical exertion, prolonged standing. Significant joint tightening, lameness, bone deformation, and weakening of ligaments and muscles during exercise. On the X-ray film, the joint space is 3 times smaller than normal, osteophytes grow, and fluid may appear in the joint cavity.
- Stage 3 - The pain becomes persistent and does not go away with rest and rest. Movement is severely restricted, possibly violating blood circulation in the joints. On the X-ray, there is little joint space, the bone is deformed sharply, and strong growth of bone tissue is noted.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Knee Arthropathy
Diagnosis of the disease includes examination of the patient and X-rays of the affected limb.
Treatment of the disease should be started as soon as possible. A thorough examination and consultation with an experienced specialist is necessary, since this disease has nonspecific symptoms and can easily be confused with other pathologies of the joint system.
The main principles of treatment, aimed at achieving a therapeutic effect:
- Eliminate knee pain;
- Improve blood circulation and accelerate the regeneration of cartilage tissue;
- Reduces pressure between joint bones;
- restore physical mobility;
- Strengthen muscles and ligaments.
ways to treat arthritis
Arthropathy can be treated both with drugs, physiotherapy, folk remedies and manual therapy.
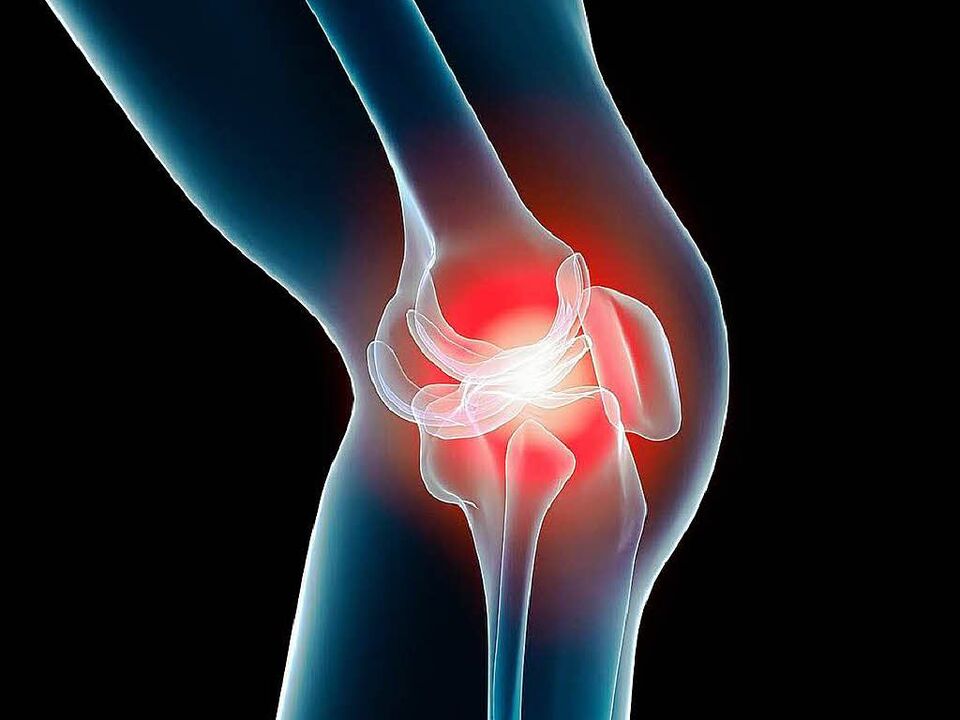
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They are traditionally used to treat inflammatory diseases of the joints. Great for pain relief, swelling and inflammation. But using these drugs only temporarily relieves symptoms and does not cure the disease itself. In addition, they have many contraindications and side effects.
- Chondroprotective agents are the most etiological treatments, they help regenerate cartilage tissue and eliminate the cause of the disease. Their use is effective in the early stages of the disease. To obtain results, long-term use of chondroprotective agents is required.
- Topical treatments - various ointments and creams - have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
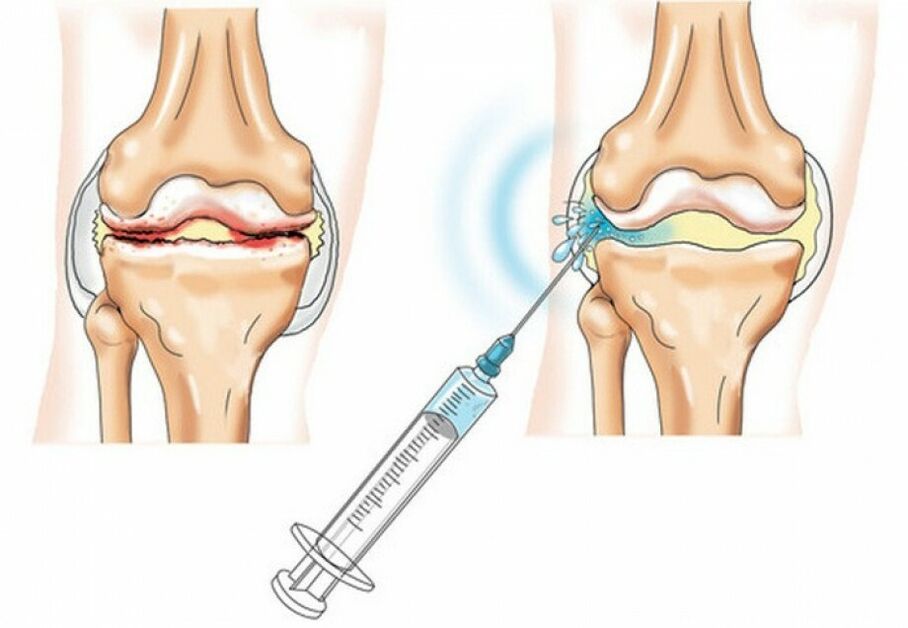
- Intra-articular injections are used to provide emergency care. The most commonly used drugs are corticosteroids. They quickly and effectively suppress pain and inflammation in the joints, but like NSAIDs, they are only symptomatic.
- Manual therapy and physiotherapy - can produce significant therapeutic effects in stages 1 and 2 of the disease.
- diet. Knee gonorrhea is known as a "salt deposit" disease. Therefore, with this disease, you need to follow a diet that excludes foods that cause salt formation. Table salt intake should be limited to 1 gram per day, meat, canned food, sweets, fat, flour.
- Walking Support - Using crutches or crutches can significantly reduce the stress on the knee joint and help with faster recovery.
- Therapeutic gymnastics is the main rehabilitation method after arthropathy treatment. Only special exercises can help restore lost mobility, strengthen muscles and ligaments, and improve blood circulation. Restoring limb function is impossible without specially designed exercises.
- Surgical treatment - in the absence of the effect of therapeutic methods, in stage 3 of the disease, severe joint deformities, surgery is necessary. Usually this is a joint replacement. This surgery allows you to regain mobility in your limb, but it has many contraindications and limitations. It is also quite expensive financially.
A complete cure for the disease is nearly impossible. To achieve stable remission of the disease, you need to follow all your doctor's recommendations, try to exercise more, do special exercises, take chondroprotective and circulation-improving drugs, and follow a diet.